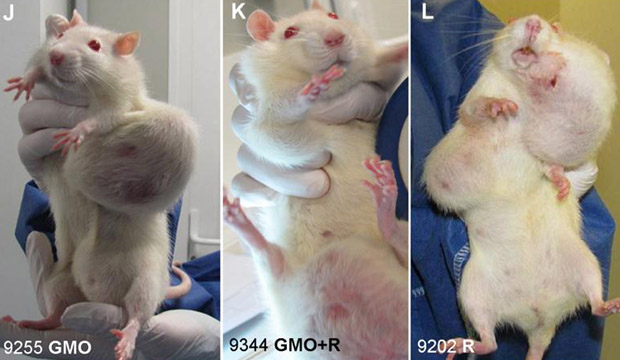
This Italian University of Urbino study found a significant lowering of nucleoplasmic and nucleolar splicing factors as well as a perichromatin granule accumulation in GM-fed mice.
Source: gmowpolsce.implesite.pl
Abstract
We carried out ultrastructural morphometrical and immunocytochemical analyses on pancreatic acinar cell nuclei from mice fed on genetically modified (GM) soybean, in order to investigate possible structural and molecular modifications of nucleoplasmic and nucleolar constituents.We found a significant lowering of nucleoplasmic and nucleolar splicing factors as well as a perichromatin granule accumulation in GM-fed mice, suggestive of reduced post-transcriptional hnRNA processing and/or nuclear export. This is in accordance to already described zymogen synthesis and processing modifications in the same animals.
Authors
M. Malatesta, M. Biggiogera, E. Manuali, M.B.L. Rocchi, B. Baldelli, G. Gazzanelli